The future of the industry in Mexico is advanced manufacturing
New technologies are being utilized by industry in Mexico to facilitate and optimize the production of a wide range of goods for foreign and domestic markets.
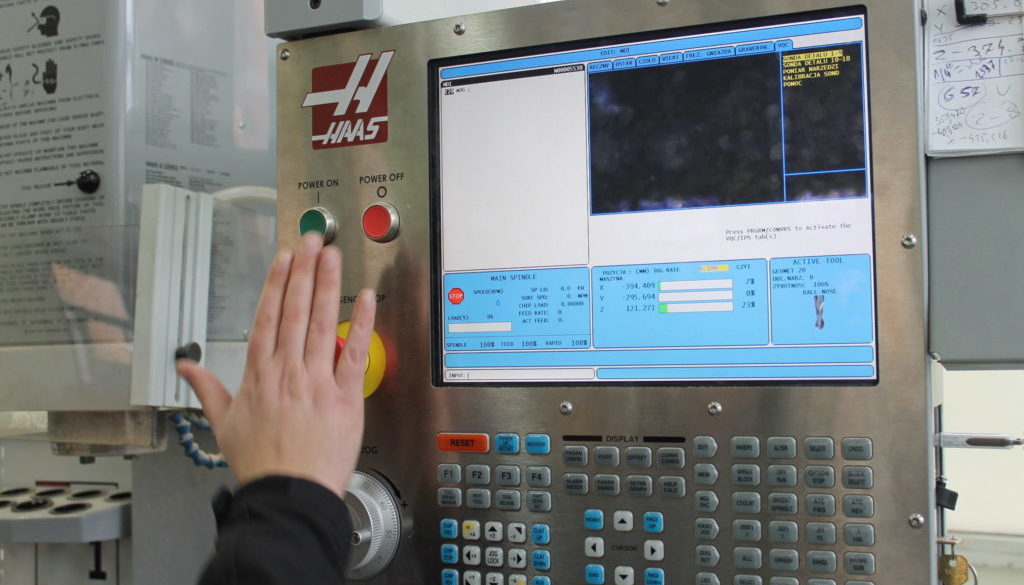
Among the trends currently found in industry in Mexico, advanced manufacturing has been quickly gaining visible ground. This type of production is increasingly encountered in Mexico’s maquiladora plants located throughout the Republic.
Given the consideration of the aforementioned, several questions must be taken into account. Among them are: What is advanced manufacturing? How does it differ from traditional manufacturing and automation? What is its presence in industry in Mexico?
According to specialists, we can see that, in the broader context of industry in Mexico, many plants in the nation’s manufacturing hubs are catching the wave of advanced manufacturing and will soon be on par with the rest of the world. Although this is positive, there are existing challenges that regional industry will need to overcome in order for this new technological trend to be beneficial for companies and not a source of difficult problems.
Advanced manufacturing: a definition
In order to define advanced manufacturing, one must return to basics and consider what traditional manufacturing consists of. According to Mexico’s Center for Advanced Technology, manufacturing, in its broadest sense, “is the process of converting raw materials into product”. Until now, industry in Mexico has primarily performed manual manufacturing that has been done by factory workers. Beyond this, advanced manufacturing includes “technology processes and those that complement the production chain”.
According to Martín Márquez, president of the Automation and Advanced Manufacturing Cluster (MACH) in Chihuahua, advanced manufacturing is the application of modern technologies for the purpose of optimizing manufacturing processes. Unlike automation, advanced manufacturing is a concept and trend of technologies applied to manufacturing, while automation is one of the specialized technologies that can be integrated into production to facilitate manufacturing processes. “It’s just the technical part of product making,” said Martín Márquez.
These technologies in industry in Mexico can have two important components: 1) processing technologies and 2) digital systems to monitor manufacturing processes. Processing technologies are varied and depend on the type of industry being considered and the class of product being made. Some of these are as follows:
- Metal printing
- 3D printing
- Mold machining
- Material characterization
- Metal stamping
- Plastic injection molding
- Heat treating
- Laser welding
- Tool selection
3D printing, for example, helps product prototyping, as it allows industry in Mexico to quickly select new materials by being able to simulate products in 3D and to perform subsequent testing on them. “Ten years ago, this was complicated because companies had to send parts to print and had to wait in order to make changes to them. Today, however, a company can print one, and “If it doesn’t look good, it can be printed again,” asserts Martín Márquez.
On the other hand, when it comes to advanced manufacturing that includes the digital systems used in industry in Mexico, these can help to measure process efficiency. Additionally, according to Martín Márquez, digital systems can have a significant impact on the production process because they enable manufacturers to generate savings, identify problems with workflow, measure the efficacy of production operations, and, also, to find ways to minimize the human and material waste that is generated by faulty manufacturing processes. It is important to keep in mind that when errors are made not only is the worker’s time wasted, but also the material that was used to make the faulty part.
Problems with advanced manufacturing encountered by industry in Mexico
The situation that Martín Marquez has observed in the maquiladora industry is that beyond automation advanced manufacturing presents a great opportunity to jump-start economic growth in the country. “Making the transition from traditional manufacturing to “mind-facturing” will not be automatic or without its downside. Changes that will necessarily be implemented to move towards an advanced manufacturing environment will result in an overall fewer number of jobs. These positions will require a properly educated and trained workforce.